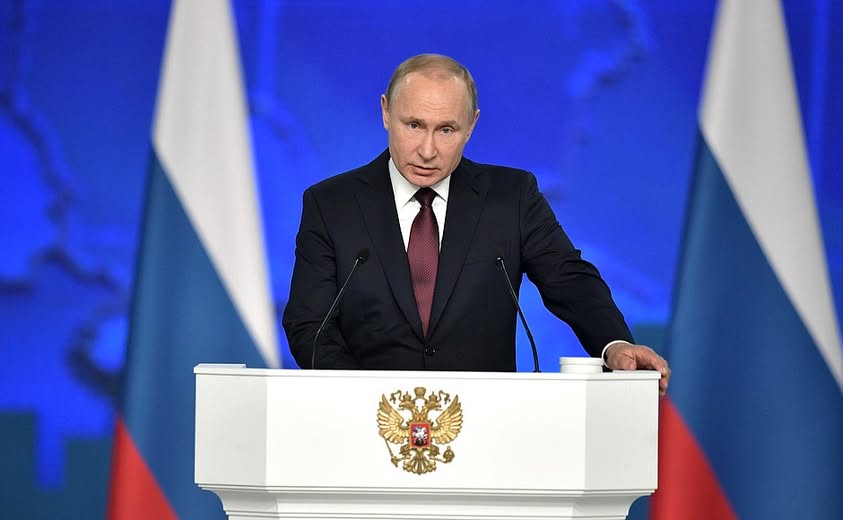
Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin is one of the most influential and controversial political figures of the 21st century. As the President of Russia, he has played a pivotal role in shaping Russia’s domestic and foreign policies. Over the years, his leadership has drawn global attention, admiration, and criticism. Putin’s career spans from the Soviet-era KGB to modern Russian governance, making him a key player in global geopolitics.
This detailed biography explores Vladimir Putin’s early life, education, political career, leadership style, economic policies, controversies, family, assets, and legacy.
Early Life and Education
Birth and Family Background
Vladimir Putin was born on October 7, 1952, in Leningrad (now Saint Petersburg), Soviet Union. His parents, Vladimir Spiridonovich Putin and Maria Ivanovna Putina, were working-class citizens who lived through World War II and the hardships of post-war Russia.
His father, Vladimir Spiridonovich Putin, served in the Soviet Navy and later worked as a factory foreman. His mother, Maria Ivanovna Putina, was a factory worker. His grandfather, Spiridon Ivanovich Putin, was reportedly a cook who served Soviet leaders, including Joseph Stalin.
Education and Early Interests
- Attended School No. 193 in Leningrad, where he showed an interest in sports, particularly judo and sambo.
- Studied Law at Leningrad State University (now Saint Petersburg State University), graduating in 1975.
- Developed a deep interest in Russian history, intelligence work, and governance.
Personal Life: Wife and Children
Marriage and Divorce
- Putin was married to Lyudmila Putina from 1983 to 2013.
- Lyudmila was a linguist and former flight attendant, who kept a relatively low public profile during their marriage.
- In 2013, the couple announced their divorce, citing the pressures of public life.
Putin’s Children
- Putin and Lyudmila have two daughters, both of whom have maintained a private life:
- Maria Vorontsova (born 1985) – A medical researcher specializing in endocrinology and genetics.
- Katerina Tikhonova (born 1986) – A scientist, academic, and former acrobatic rock’n’roll dancer.
- Speculations exist about Putin having additional children, but there is no official confirmation.
Putin’s Economic Policies and Russia’s Development
Early Economic Reforms (2000-2008)
- Focused on stabilizing Russia’s economy after the turbulent 1990s.
- Implemented tax reforms, including a flat income tax rate of 13%, attracting foreign investments.
- Oversaw large-scale privatization of industries while increasing state control over strategic sectors like energy and defense.
- Benefited from rising oil and gas prices, which significantly boosted Russia’s GDP.
- Paid off a large portion of Russia’s foreign debt, reducing reliance on international financial institutions.
Energy Dominance and Infrastructure Growth
- Strengthened Russia’s position as a leading energy exporter, particularly in oil and natural gas.
- Developed key pipeline projects such as Nord Stream and TurkStream, increasing Russia’s influence in European energy markets.
- Launched large-scale infrastructure projects, including modernizing roads, railways, and urban centers.
Economic Challenges and Western Sanctions (2014-Present)
- Faced economic downturns following the annexation of Crimea in 2014, leading to Western sanctions.
- Shifted focus to self-sufficiency, promoting agriculture, defense industries, and high-tech development.
- Strengthened economic ties with China, India, and Middle Eastern countries to reduce dependency on Western markets.
- Implemented the National Projects initiative (2019-2024), focusing on healthcare, education, infrastructure, and digital economy.
- Despite sanctions, Russia maintained low unemployment rates and moderate inflation but suffered from reduced foreign investments.
Putin’s Net Worth and Assets
Official vs. Estimated Wealth
- Officially, Putin’s declared income is modest, but numerous reports suggest he has vast hidden wealth.
- Some estimates claim his net worth exceeds $200 billion, making him one of the wealthiest individuals in the world.
Major Assets and Luxury Holdings
- Palaces and Residences: Allegedly owns Putin’s Palace, a luxurious estate on the Black Sea, reportedly worth over $1 billion.
- Yachts and Aircraft: Reported to have access to private jets, luxury yachts, and high-end vehicles.
- Oligarch-Controlled Wealth: Many believe that much of Putin’s wealth is hidden through Russian oligarchs and offshore accounts.
- Real Estate Holdings: Allegedly has vast land holdings, apartments, and estates across Russia and abroad.
Russia-Ukraine War and Putin’s Role
Background and Justification
- In February 2022, Vladimir Putin launched a full-scale invasion of Ukraine, escalating the conflict that began in 2014 with the annexation of Crimea.
- Justified the invasion by claiming Ukraine was under Western influence and that Russia needed to protect its national security interests.
- Framed the conflict as a “special military operation”, stating that NATO expansion posed a threat to Russia.
Global Impact and Consequences
- Economic Fallout: Sanctions have weakened Russia’s economy, reducing foreign investment and impacting energy exports.
- Diplomatic Isolation: Russia has faced UN resolutions, diplomatic expulsions, and reduced global influence.
- Military Casualties: Both Russian and Ukrainian forces have suffered heavy losses, with thousands of civilian casualties reported.
- Shifting Alliances: Strengthened Russia’s ties with China, Iran, and North Korea, while distancing it from the West.
Legacy and Future Prospects
- Remains a dominant figure in Russian and global politics.
- Expected to continue shaping Russia’s economic, military, and foreign policy.
- Faces growing internal and international opposition but maintains firm control over Russia’s governance.
Conclusion
Vladimir Putin’s leadership has redefined modern Russia, influencing global politics and diplomacy. While praised for stabilizing the country and expanding its geopolitical reach, his governance is also criticized for authoritarianism, human rights abuses, and military aggression. His legacy will remain a subject of global debate, shaping the course of Russia’s future for years to come.